15 Out Of 25 Percentage
plugunplug
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
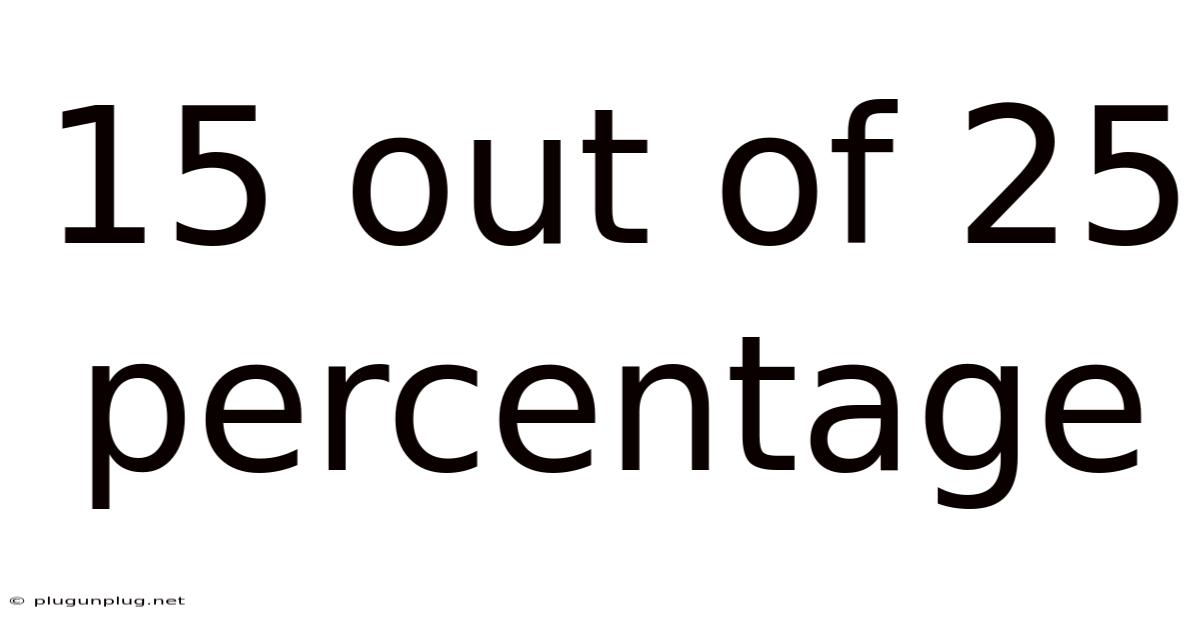
Table of Contents
Understanding and Interpreting 15 out of 25: A Comprehensive Guide
Obtaining a score of 15 out of 25 on a test, quiz, or assignment is a common experience for many students. Understanding what this score represents, its implications, and how to improve upon it requires a nuanced approach. This article will delve deep into the meaning of 15/25, exploring its percentage equivalent, contextual implications, strategies for improvement, and frequently asked questions. We'll examine how to interpret this score in various academic settings and provide practical advice for both students and educators.
Understanding the Percentage Equivalent
The first step in interpreting 15 out of 25 is to convert it into a percentage. This provides a standardized measure that allows for easier comparison across different assessments. To calculate the percentage, we use the following formula:
(Score / Total Score) x 100%
In this case: (15 / 25) x 100% = 60%
A score of 15 out of 25 is therefore equivalent to 60%. This is a passing grade in many educational systems, but its significance depends heavily on the context.
Contextual Implications: What Does 60% Mean?
A 60% score doesn't exist in a vacuum. Its meaning is heavily influenced by several factors:
-
The Specific Assessment: Was it a major exam, a smaller quiz, a homework assignment, or a project? A 60% on a final exam carries far more weight than a 60% on a minor assignment.
-
The Subject Matter: A 60% in a challenging subject like advanced calculus might reflect a stronger understanding than a 60% in a less demanding subject.
-
Individual Performance: How does this score compare to your previous performance in the same subject? A 60% representing a significant improvement indicates progress, while a 60% following a series of higher scores might signify a decline that needs attention.
-
Grading Rubric: Understanding the specific grading rubric used is crucial. Some rubrics might assign higher weight to certain aspects of the assessment, meaning that a 60% might still indicate proficiency in key areas even if it doesn't meet the overall target.
-
Class Average: Comparing your score to the class average provides further context. If your 60% is above average, it demonstrates relative strength in the subject. However, if it is below average, it highlights areas for improvement.
Analyzing the Score: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
Achieving a 60% score provides valuable insights into your strengths and weaknesses. Instead of focusing solely on the numerical value, analyze the specific questions or tasks you answered correctly and incorrectly. This detailed analysis can pinpoint areas where you excel and areas requiring further attention.
-
Review Correct Answers: Examine the questions you answered correctly. Identify the concepts and skills you demonstrated mastery of. This helps reinforce your strengths and build confidence.
-
Analyze Incorrect Answers: This is crucial. Don't just accept that you got the answers wrong; understand why they were wrong. Did you misunderstand the concepts? Were there calculation errors? Did you misread the questions? Identifying the root cause of each mistake is key to improvement.
-
Seek Feedback: If possible, seek feedback from your teacher or instructor. They can provide valuable insights into your performance and offer specific guidance for improvement.
Strategies for Improvement: From 60% to Higher Scores
Improving your scores requires a multifaceted approach. It's not simply about memorizing information; it's about developing a deeper understanding of the subject matter and refining your study habits.
-
Active Recall: Instead of passively rereading notes, actively test your knowledge. Use flashcards, practice questions, or teach the material to someone else. This forces your brain to actively retrieve information, solidifying your understanding.
-
Spaced Repetition: Review the material at increasing intervals. This combats the forgetting curve and ensures long-term retention.
-
Effective Note-Taking: Develop a consistent note-taking system that allows you to easily organize and review the material. Experiment with different methods to find what works best for you. Mind mapping, Cornell notes, or outlining can all be effective.
-
Seek Clarification: Don't hesitate to ask for help when you're struggling. Talk to your teacher, classmates, or tutors to clarify any concepts you don't understand.
-
Time Management: Effective time management is crucial for academic success. Create a study schedule that allocates sufficient time to each subject. Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable chunks.
-
Study Environment: Create a conducive study environment that is free from distractions. Find a quiet space where you can focus and concentrate.
-
Practice Problems: For subjects that require problem-solving skills (such as mathematics or science), practice is essential. Work through numerous problems to build your skills and identify areas where you need improvement.
-
Understanding vs. Memorization: Shift your focus from rote memorization to a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts. Focus on why things are the way they are, not just what they are.
The Role of the Teacher or Instructor
Teachers play a vital role in helping students understand their scores and improve their performance. Effective feedback should go beyond simply providing a numerical grade. It should include:
-
Specific Feedback on Strengths and Weaknesses: Teachers should identify the areas where students excelled and areas requiring improvement. This targeted feedback is far more effective than general comments.
-
Strategies for Improvement: Teachers should provide concrete suggestions for how students can improve their understanding and performance. This might involve recommending specific resources, providing extra practice problems, or suggesting different learning strategies.
-
Individualized Support: Teachers should offer personalized support to students who are struggling. This could involve one-on-one tutoring, extra help sessions, or access to supplementary materials.
-
Constructive Criticism: Feedback should be constructive and encouraging, focusing on growth and improvement rather than simply pointing out mistakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is 60% a good grade?
A: Whether 60% is a good grade depends on the context. In some systems, it might be a passing grade, while in others it might be considered unsatisfactory. The specific assessment, subject matter, and individual performance all play a role in determining the significance of a 60% score.
Q: How can I improve my score from 60% to 80% or higher?
A: Improving your score requires a dedicated effort to understand the material deeply, refine your study habits, and seek help when needed. Implementing the strategies discussed earlier – active recall, spaced repetition, effective note-taking, and seeking clarification – are key to achieving significant improvement.
Q: What if I consistently score around 60%?
A: Consistently scoring around 60% indicates a need for a more significant shift in your approach to learning. Seek help from your teacher, tutor, or academic advisor to identify underlying issues and develop a more effective learning strategy. This might involve addressing learning disabilities, improving time management skills, or developing better study habits.
Q: Can a 60% still be considered a success?
A: Yes, a 60% can be considered a success in certain contexts. If it represents a significant improvement over previous performance, or if it's above the class average, it can be viewed as progress. The key is to focus on the growth and learning that occurred, not just the numerical grade itself.
Conclusion: Learning from the Score
A score of 15 out of 25, or 60%, offers a valuable opportunity for learning and improvement. Instead of viewing it as a simple numerical grade, treat it as feedback that provides insights into your strengths and weaknesses. By carefully analyzing your performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing effective learning strategies, you can transform a 60% into a stepping stone towards greater academic success. Remember that consistent effort, a willingness to learn from mistakes, and seeking help when needed are key ingredients in achieving your academic goals. Focus on understanding the underlying concepts, not just memorizing facts, and you will see substantial growth in your overall academic performance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Drops In Milliliter
Sep 23, 2025
-
Hitlers Aims In Foreign Policy
Sep 23, 2025
-
How Many Weeks Ina Year
Sep 23, 2025
-
Adult Stem Cells Vs Embryonic
Sep 23, 2025
-
Convert 75 Cm To Inches
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 Out Of 25 Percentage . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.