160 Degrees C In F
plugunplug
Sep 04, 2025 · 6 min read
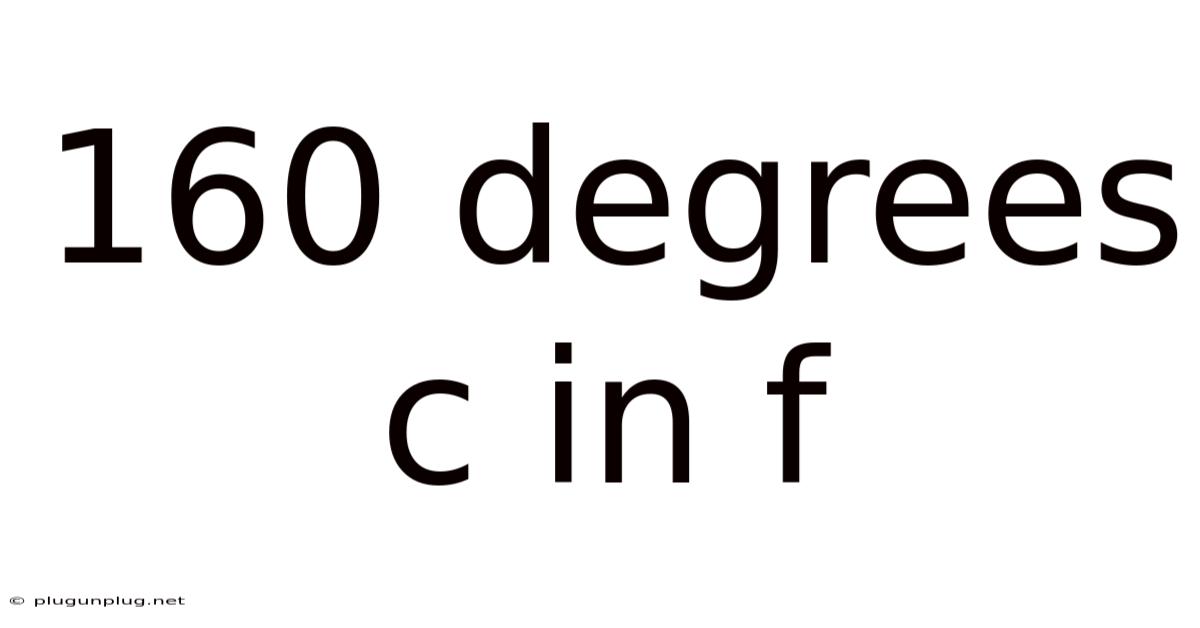
Table of Contents
160 Degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit? Understanding these different temperature scales is crucial in various fields, from cooking and baking to scientific research and everyday life. This comprehensive guide will not only teach you how to convert 160 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit but also delve deeper into the underlying principles of these temperature scales, providing you with the knowledge and tools to make future conversions with confidence. We'll explore practical applications and even address some frequently asked questions.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's establish a foundational understanding of both scales. The Celsius scale (°C), also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric unit based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. This creates a simple and readily understandable scale.
The Fahrenheit scale (°F), on the other hand, is an imperial unit with a more complex history. Its zero point is based on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, and the boiling point of water is set at 212°F. This results in a scale where 0°F is significantly colder than 0°C.
The difference in scale and zero points necessitates a conversion formula when switching between the two systems.
Converting 160 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
The standard formula for converting Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's apply this formula to convert 160°C to °F:
°F = (160°C × 9/5) + 32
°F = (288) + 32
°F = 320
Therefore, 160 degrees Celsius is equal to 320 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications of 160°C (320°F)
Understanding the equivalent of 160°C in Fahrenheit has numerous practical applications across various fields. Let's explore a few:
-
Cooking and Baking: This temperature range is crucial in many culinary processes. 320°F is a common temperature for deep-frying certain foods, ensuring a crispy exterior and a tender interior. It's also used in some baking techniques, although ovens usually use ranges rather than precise settings. Knowing this equivalent is vital for achieving desired cooking results when using recipes from different countries or regions that might use different temperature scales.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes operate at high temperatures. Understanding the conversion is essential for maintaining consistent operating conditions. This is particularly important in industries like manufacturing, where precise temperature control is crucial for the quality of the final product. For instance, certain types of plastics require processing at temperatures around 320°F.
-
Scientific Research: In laboratories and scientific research, accurate temperature measurements are paramount. Researchers often work with equipment calibrated in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, requiring a clear understanding of how to convert between the two scales to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Thermodynamic studies, material science experiments, and chemical reactions all rely on precise temperature control and conversion.
-
Everyday Life: While less frequent than in other fields, knowing the equivalent can be helpful in everyday situations. For example, if you're using a foreign appliance or reading an instruction manual written in a different system, you'll need to convert the temperature to your familiar scale to understand the appliance's settings.
Beyond the Conversion: A Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales
The simple conversion formula masks a deeper understanding of the different scales and their histories. While the conversion itself is straightforward, grasping the underlying differences between Celsius and Fahrenheit offers a more complete understanding of temperature measurement.
-
The Origins of Fahrenheit: The Fahrenheit scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. His original scale was based on three fixed points: the temperature of a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride (0°F), the temperature of water and ice (32°F), and the temperature of the human body (96°F – later revised to 98.6°F). The scale's arbitrary zero point and the use of body temperature as a reference point highlight a different approach to temperature measurement compared to the more systematic Celsius scale.
-
The Advantages of Celsius: The Celsius scale's advantage lies in its direct relation to the freezing and boiling points of water. This inherent connection makes it a more intuitive and easily understood scale, particularly in scientific contexts. The 100-degree range between freezing and boiling also simplifies calculations and comparisons.
-
The Persistence of Fahrenheit: Despite the Celsius scale's scientific advantages, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in some parts of the world, particularly in the United States. The continued use of Fahrenheit reflects historical inertia and cultural factors.
Understanding Temperature: More Than Just Numbers
Temperature isn't simply a number; it represents the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Higher temperatures indicate greater kinetic energy, meaning the particles are moving faster. This fundamental understanding links temperature scales to the underlying physical properties of matter. Converting between scales doesn't just change the number; it translates the description of this particle movement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I use an online converter instead of the formula? A: Yes, numerous online converters are readily available. However, understanding the formula provides a deeper understanding of the conversion process and allows you to perform calculations without relying on external tools.
-
Q: What happens if I input a negative Celsius value into the conversion formula? A: The formula works for negative Celsius temperatures as well. It will accurately convert negative Celsius values into their Fahrenheit equivalents. Remember that temperatures below 0°C are below the freezing point of water.
-
Q: Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius and Fahrenheit? A: Yes, several other temperature scales exist, including Kelvin (K), Rankine (R), and Rømer (° Rø). Kelvin is the absolute temperature scale, widely used in scientific applications.
-
Q: Why is precision important in temperature conversions? A: Precision in temperature conversions is vital in many applications, especially in scientific experiments, industrial processes, and cooking. Inaccurate conversions can lead to errors, potentially causing damage, inconsistencies, or safety hazards.
Conclusion
Converting 160 degrees Celsius to 320 degrees Fahrenheit is a simple calculation, but the underlying principles of temperature measurement and the historical context of different scales provide a richer understanding. This knowledge is not just useful for performing conversions but also for appreciating the broader scientific context of temperature and its significance in various aspects of our lives. From everyday cooking to advanced scientific research, understanding temperature scales and their conversion is essential for accuracy, efficiency, and safety. With a grasp of the formula and the underlying principles, you're now equipped to tackle temperature conversions confidently and effectively.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Work Plan
Sep 12, 2025
-
Words For The Dash Poem
Sep 12, 2025
-
73 Kg How Many Pounds
Sep 12, 2025
-
Definition Of Grave In Music
Sep 12, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry Regular Pentagon
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 160 Degrees C In F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.