2 3 X 3 2
plugunplug
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
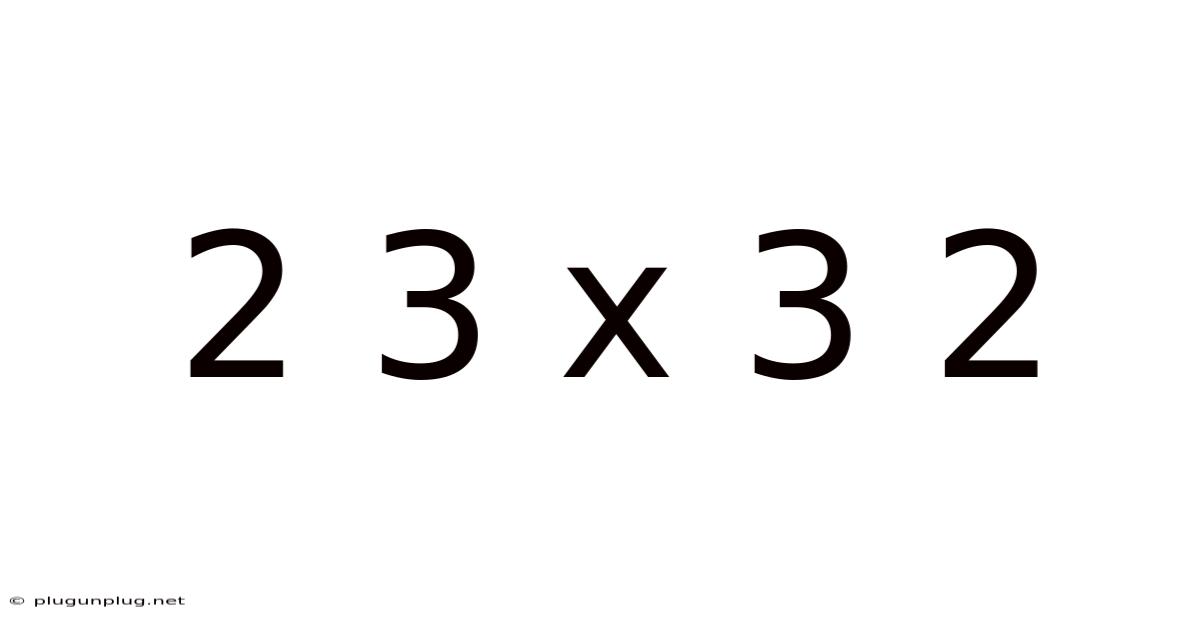
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into 2³ x 3²
The seemingly simple expression "2³ x 3²" might appear straightforward at first glance. However, this mathematical phrase offers a rich opportunity to explore fundamental concepts in arithmetic, algebra, and even touches upon the broader realms of number theory and computational thinking. This article will not only provide a clear explanation of how to solve this expression but also delve into its underlying principles, demonstrating its relevance across various mathematical contexts. We'll unpack the meaning of exponents, explore the order of operations, and discuss the significance of prime factorization – ultimately unveiling the elegance hidden within this concise equation.
Understanding Exponents and Their Significance
Before tackling 2³ x 3², let's solidify our understanding of exponents. An exponent, also known as a power or index, indicates how many times a base number is multiplied by itself. In the expression a<sup>b</sup>, 'a' represents the base, and 'b' represents the exponent. So, a<sup>b</sup> means 'a' multiplied by itself 'b' times.
For instance:
-
2³ means 2 x 2 x 2 = 8. Here, 2 is the base, and 3 is the exponent. We read this as "two cubed" or "two raised to the power of three."
-
3² means 3 x 3 = 9. Here, 3 is the base, and 2 is the exponent. We read this as "three squared" or "three raised to the power of two."
Exponents are fundamental to many areas of mathematics, from simple calculations to complex scientific formulas. They provide a concise way to represent repeated multiplication, simplifying equations and making them easier to understand and manipulate.
Order of Operations: PEMDAS/BODMAS
The order of operations, often remembered by the acronyms PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction), dictates the sequence in which we perform calculations. This is crucial to ensure we arrive at the correct answer. In our expression, 2³ x 3², exponents come before multiplication.
Step-by-Step Solution of 2³ x 3²
Following the order of operations:
-
Evaluate the Exponents: First, we calculate 2³ and 3². As established earlier:
- 2³ = 2 x 2 x 2 = 8
- 3² = 3 x 3 = 9
-
Perform the Multiplication: Now, substitute the results back into the original expression:
- 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9
-
Final Calculation: Finally, multiply 8 by 9:
- 8 x 9 = 72
Therefore, the solution to 2³ x 3² is 72.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The result, 72, can be further analyzed through prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. This decomposition reveals the fundamental building blocks of a number.
To find the prime factorization of 72:
- We can start by dividing 72 by the smallest prime number, 2: 72 ÷ 2 = 36
- Divide 36 by 2: 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- Divide 18 by 2: 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- Now, 9 is not divisible by 2, but it is divisible by the next prime number, 3: 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- Finally, 3 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 72 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, which can be written more concisely as 2³ x 3². This elegantly demonstrates that our initial expression, 2³ x 3², is simply a different representation of the prime factorization of 72. This connection highlights the interconnectedness of various mathematical concepts.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
While seemingly abstract, the principles involved in solving 2³ x 3² have practical applications in various fields:
-
Computer Science: Binary representation (base-2) relies heavily on exponents of 2. Understanding exponents is crucial for comprehending data storage, memory management, and algorithmic complexity.
-
Physics and Engineering: Many physical phenomena, such as radioactive decay and compound interest, are modeled using exponential functions.
-
Finance: Compound interest calculations, crucial for understanding investment growth, leverage the power of exponents.
-
Geometry: Calculating volumes and surface areas of three-dimensional shapes often involves exponents.
Expanding the Concept: Exploring Variations
Let's consider variations of the original expression to further solidify our understanding:
-
What if the expression was 2³ + 3²? Following PEMDAS, we'd first calculate the exponents: 2³ = 8 and 3² = 9. Then we would add them: 8 + 9 = 17. This illustrates the importance of correctly interpreting the operation signs.
-
What if the expression was (2 x 3)²? Here, the parentheses dictate the order of operations. First, we perform the multiplication inside the parentheses: 2 x 3 = 6. Then we square the result: 6² = 36. This highlights how parentheses significantly alter the outcome.
-
What if we had a more complex expression involving multiple exponents and operations? The principle remains the same: always adhere to the PEMDAS/BODMAS rule. Work through the exponents first, then multiplication and division (from left to right), and finally addition and subtraction (from left to right).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is the order of operations important?
A1: The order of operations ensures consistency in mathematical calculations. Without a defined order, different individuals could arrive at different answers for the same expression, leading to confusion and errors.
Q2: What happens if I don't follow the order of operations?
A2: Not following the order of operations will likely lead to an incorrect answer. For instance, if you multiply 2 and 3 before calculating the exponents in 2³ x 3², you'll get a completely different and wrong result.
Q3: Can I use a calculator to solve this?
A3: Yes, most calculators will automatically follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS). However, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for solving more complex problems and for grasping the fundamental concepts of arithmetic and algebra.
Q4: Are there other ways to represent 72?
A4: Yes, 72 can be represented in numerous ways, including different factorizations (e.g., 8 x 9, 6 x 12, 4 x 18), as a sum of various numbers, or even in different bases (e.g., binary, hexadecimal).
Conclusion: Beyond the Numbers
The seemingly simple expression 2³ x 3² offers a gateway to exploring fundamental mathematical concepts, reinforcing the importance of the order of operations, and unveiling the elegance of prime factorization. By understanding the underlying principles, we not only solve the expression but also gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. This example extends beyond a mere calculation; it serves as a stepping stone towards a more comprehensive understanding of arithmetic, algebra, and the foundations of mathematics. The ability to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, as demonstrated with this expression, is a crucial skill applicable across various academic and professional disciplines. Remember, the journey of understanding is often more valuable than the destination itself.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 3 X 3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.