38/14 As A Mixed Number
plugunplug
Sep 07, 2025 · 5 min read
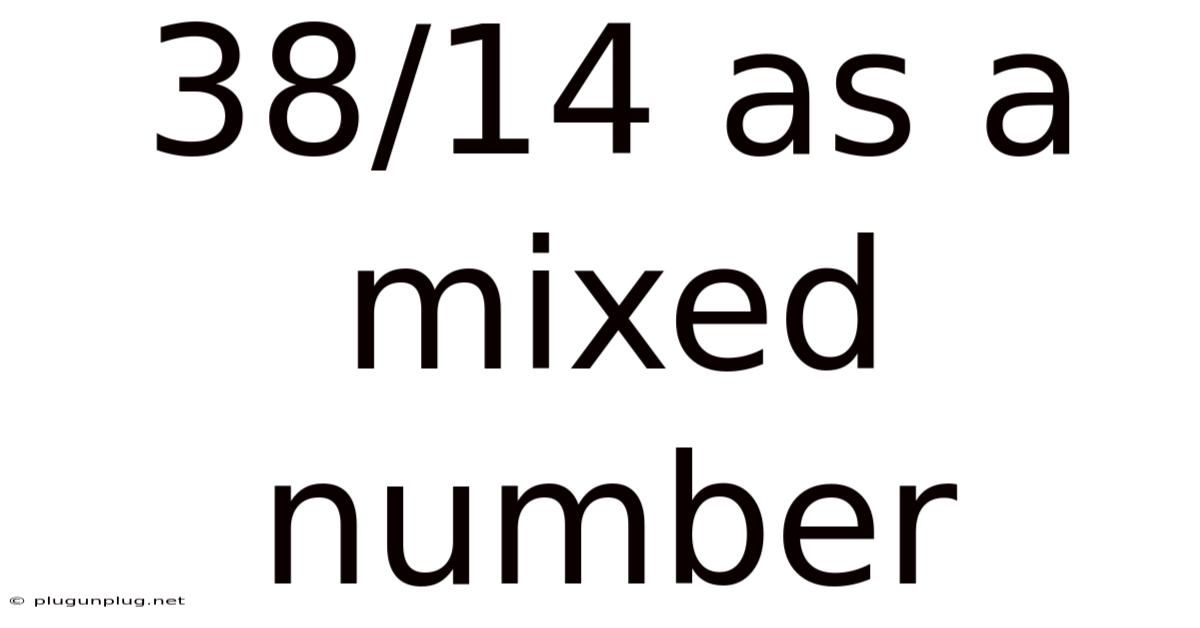
Table of Contents
Understanding 38/14 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The conversion of improper fractions, like 38/14, into mixed numbers is a fundamental concept in arithmetic. This seemingly simple process underpins a deeper understanding of fractions, laying the groundwork for more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 38/14 into a mixed number but also delve into the underlying principles, providing you with a solid grasp of the topic. We will explore various methods, address common questions, and explore the practical applications of this essential skill.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the definition. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number), like 1/2 or 3/4. For example, 2 1/3 is a mixed number, representing two whole units and one-third of another unit. Improper fractions, conversely, have a numerator larger than or equal to the denominator, such as 7/4 or 38/14.
Converting 38/14 to a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step Guide
There are two primary methods for converting an improper fraction to a mixed number:
Method 1: Division
This is the most straightforward method. We simply divide the numerator by the denominator.
-
Divide: Divide the numerator (38) by the denominator (14). 38 ÷ 14 = 2 with a remainder of 10.
-
Whole Number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the whole number is 2.
-
Fraction: The remainder (10) becomes the numerator of the fraction, and the original denominator (14) remains the denominator. This gives us the fraction 10/14.
-
Simplify (if possible): Always simplify the fraction to its lowest terms. Both 10 and 14 are divisible by 2. Therefore, 10/14 simplifies to 5/7.
-
Combine: Combine the whole number and the simplified fraction to form the mixed number. Thus, 38/14 as a mixed number is 2 5/7.
Method 2: Repeated Subtraction
This method provides a more intuitive understanding of the process, particularly helpful for visualizing the concept.
-
Subtract the denominator: Repeatedly subtract the denominator (14) from the numerator (38) until the result is less than the denominator.
- 38 - 14 = 24
- 24 - 14 = 10
-
Count the subtractions: The number of times you subtracted the denominator represents the whole number part of the mixed number. We subtracted 14 twice, so the whole number is 2.
-
Remainder: The remaining number after the repeated subtractions becomes the numerator of the fraction. The remainder is 10.
-
Fraction: Use the original denominator (14) as the denominator of the fraction. This gives us 10/14.
-
Simplify: Simplify the fraction 10/14 to 5/7.
-
Combine: Combine the whole number and the simplified fraction to get the mixed number: 2 5/7.
Understanding the Mathematical Principles
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is based on the fundamental concept of dividing a quantity into groups. In the case of 38/14, we are essentially asking, "How many times does 14 go into 38?" The division process answers this question. The quotient represents the number of complete groups (whole numbers), and the remainder represents the portion of a group that's left over (the fraction).
Why Simplify Fractions?
Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms. This is essential for several reasons:
- Clarity: Simplified fractions are easier to understand and work with. 5/7 is clearly simpler than 10/14.
- Consistency: In mathematics, consistency is crucial. Simplifying fractions ensures uniformity in representing values.
- Efficiency: Simplified fractions are more efficient in calculations and problem-solving.
Practical Applications
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers has widespread applications in various fields:
- Cooking and Baking: Recipes often use mixed numbers to specify ingredient quantities.
- Construction and Engineering: Measurements in construction and engineering frequently involve mixed numbers.
- Everyday Life: Dividing items or resources often results in improper fractions that need to be converted for practical understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if the remainder is zero? If the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator, the improper fraction is already a whole number. For example, 14/14 = 1.
-
Can I convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction? Yes, absolutely. To convert a mixed number (like 2 5/7) back to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. This result becomes the new numerator, while the denominator remains the same. In this case: (2 * 7) + 5 = 19, resulting in the improper fraction 19/7.
-
Are there other ways to convert improper fractions? While division and repeated subtraction are the most common methods, visual representations like using fraction bars or area models can aid understanding, particularly for visual learners.
-
Why is simplifying important in this context? Simplifying is crucial for providing the most concise and readily understandable representation of the quantity. An unsimplified answer, while technically correct, is less elegant and can be more challenging to use in further calculations.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 38/14 to a mixed number is a vital skill in mathematics. Understanding the underlying principles of division and the importance of simplification ensures accuracy and efficiency. Whether you use the division method or the repeated subtraction method, the result remains the same: 2 5/7. This skill not only enhances your mathematical proficiency but also provides a foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems in various fields. Remember, practice makes perfect! The more you work with fractions, the more intuitive and effortless this conversion will become. Mastering this fundamental concept will undoubtedly boost your confidence and prepare you for more advanced mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 38/14 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.