5 2/9 - 3 3/5
plugunplug
Sep 05, 2025 · 6 min read
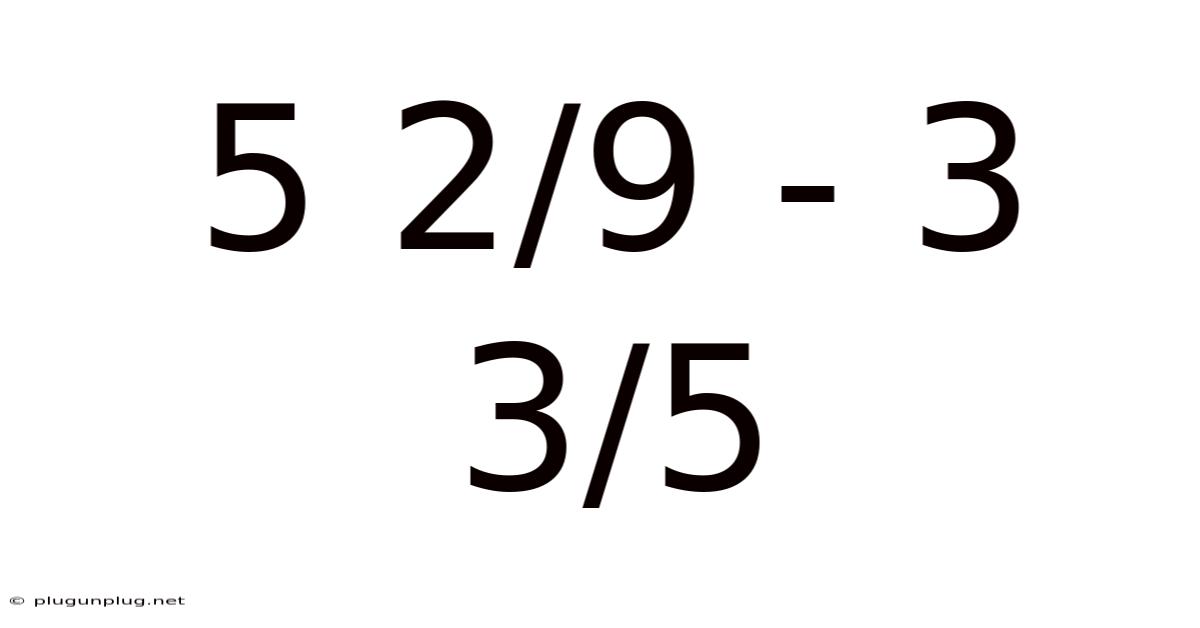
Table of Contents
Deconstructing Subtraction: A Deep Dive into 5 2/9 - 3 3/5
Subtracting mixed numbers might seem daunting at first, but with a structured approach and a solid understanding of fractions, it becomes a manageable and even enjoyable mathematical process. This article will guide you through the subtraction of 5 2/9 and 3 3/5, explaining each step in detail, and providing insights that extend beyond this specific problem. We'll explore the underlying concepts, offer alternative methods, and address frequently asked questions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of mixed number subtraction. This detailed explanation will cover the core concepts, making it easily understandable and searchable (for example, searches like "subtracting mixed numbers," "fraction subtraction," or "5 2/9 minus 3 3/5").
Understanding Mixed Numbers
Before diving into the subtraction, let's solidify our understanding of mixed numbers. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator). For example, 5 2/9 represents five whole units and two-ninths of another unit. Similarly, 3 3/5 represents three whole units and three-fifths of another unit.
Understanding the relationship between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. We can convert a mixed number into an improper fraction and vice-versa. To convert 5 2/9 into an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number (5) by the denominator (9), add the numerator (2), and keep the same denominator: (5 * 9) + 2 = 47, so 5 2/9 = 47/9. Similarly, 3 3/5 converts to (3 * 5) + 3 = 18, so 3 3/5 = 18/5.
Step-by-Step Subtraction: 5 2/9 - 3 3/5
Now, let's tackle the subtraction: 5 2/9 - 3 3/5. The direct subtraction of these mixed numbers isn't straightforward because the fractions have different denominators. Our first step is to find a common denominator.
1. Finding the Least Common Denominator (LCD):
The denominators are 9 and 5. To find the LCD, we find the least common multiple (LCM) of 9 and 5. Since 9 and 5 are relatively prime (they share no common factors other than 1), their LCM is simply their product: 9 * 5 = 45. Therefore, our common denominator is 45.
2. Converting to Equivalent Fractions:
We now convert both fractions to equivalent fractions with a denominator of 45:
- For 2/9, we multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 5: (2 * 5) / (9 * 5) = 10/45
- For 3/5, we multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 9: (3 * 9) / (5 * 9) = 27/45
Our equation now becomes: 5 10/45 - 3 27/45
3. Addressing the Subtraction Challenge:
Notice that we now have 10/45 - 27/45. We cannot directly subtract a larger fraction from a smaller one. This necessitates borrowing from the whole number part.
4. Borrowing from the Whole Number:
We borrow 1 from the 5, leaving us with 4. This borrowed 1 is then converted into a fraction with the common denominator (45): 45/45. We add this to the existing fraction: 10/45 + 45/45 = 55/45.
Our equation now transforms into: 4 55/45 - 3 27/45
5. Subtracting the Fractions and Whole Numbers:
Now, we can subtract the fractions and the whole numbers separately:
- Whole numbers: 4 - 3 = 1
- Fractions: 55/45 - 27/45 = 28/45
6. Combining the Result:
Combining the results, we get our final answer: 1 28/45
Therefore, 5 2/9 - 3 3/5 = 1 28/45
Alternative Method: Converting to Improper Fractions
An alternative approach involves converting both mixed numbers into improper fractions first, then performing the subtraction, and finally converting the result back into a mixed number.
1. Converting to Improper Fractions:
As calculated earlier: 5 2/9 = 47/9 and 3 3/5 = 18/5
2. Finding a Common Denominator:
The common denominator for 9 and 5 is still 45.
3. Converting to Equivalent Improper Fractions:
- 47/9 * 5/5 = 235/45
- 18/5 * 9/9 = 162/45
4. Subtracting the Improper Fractions:
235/45 - 162/45 = 73/45
5. Converting Back to a Mixed Number:
To convert 73/45 back into a mixed number, we divide 73 by 45: 73 ÷ 45 = 1 with a remainder of 28. This means 73/45 = 1 28/45
The result is the same as before: 1 28/45. This confirms the accuracy of our calculations using both methods.
The Importance of Understanding the Underlying Concepts
This seemingly simple subtraction problem highlights the importance of understanding fundamental concepts in arithmetic. Proficiency in finding common denominators, converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions, and the process of borrowing are essential skills for various mathematical operations. These are not isolated techniques; they form the building blocks for more complex calculations in algebra, calculus, and other advanced mathematical fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use a calculator for this type of problem?
A: While calculators can provide the answer, understanding the process is crucial. Calculators don't teach you the underlying mathematical principles, which are essential for problem-solving and critical thinking. Using a calculator for this problem negates the learning opportunity.
Q: What if the fractions were more complex, with larger numbers?
A: The process remains the same. The key is to systematically follow the steps: find the LCD, convert to equivalent fractions, borrow if necessary, subtract the fractions and whole numbers, and finally convert the result back into a simplified mixed number if needed.
Q: Are there any shortcuts for finding the LCD?
A: For smaller numbers, finding the LCM by listing multiples is straightforward. For larger numbers, prime factorization can be a more efficient method. This involves breaking down each number into its prime factors and then taking the highest power of each prime factor to construct the LCM.
Conclusion
Subtracting mixed numbers like 5 2/9 - 3 3/5 may seem challenging initially, but by breaking down the problem into smaller, manageable steps and understanding the fundamental principles of fractions and mixed numbers, it becomes a straightforward process. This article has explored two methods to solve this problem, emphasizing the importance of mastering fundamental concepts. The ability to perform these calculations accurately and efficiently is not only crucial for academic success but also for practical applications in various fields. Remember, the key is to approach each step methodically, ensuring a clear and accurate understanding throughout the process. Practice is key to mastering this skill and building a strong foundation in mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 2/9 - 3 3/5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.