7 X 2 X 3
plugunplug
Sep 07, 2025 · 6 min read
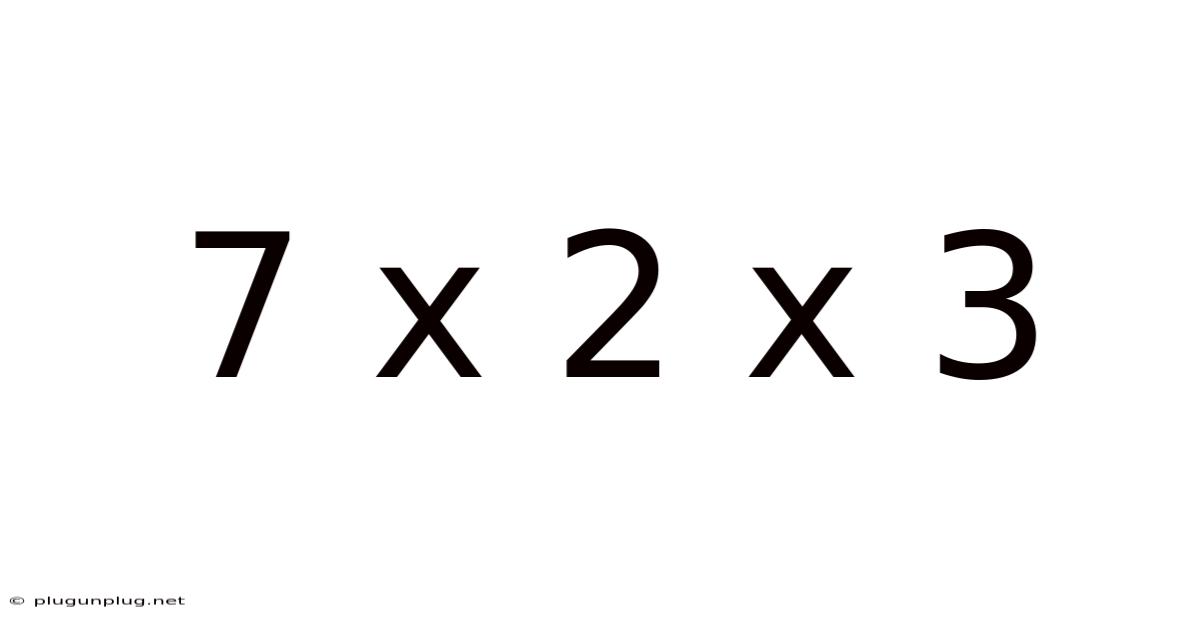
Table of Contents
Decoding 7 x 2 x 3: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "7 x 2 x 3," delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying principles of multiplication, its practical applications in various fields, and its significance in developing a strong foundation in mathematics. We will unpack the concept of multiplication, explore different methods for solving the problem, and examine its real-world relevance, making this a comprehensive guide for students and anyone interested in enhancing their mathematical understanding. This exploration will include discussions on factors, multiples, prime numbers, and the commutative and associative properties of multiplication, ensuring a thorough and engaging learning experience.
Understanding the Basics: What is Multiplication?
At its core, multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation representing repeated addition. When we say "7 x 2 x 3," we are essentially saying "add seven to itself twice, and then multiply the result by three." This seemingly simple operation forms the bedrock of countless mathematical concepts and practical applications. Understanding multiplication is crucial for tackling more complex mathematical problems, from algebra and calculus to data analysis and scientific modeling. The numbers involved – 7, 2, and 3 – are called factors. The result of the multiplication is called the product.
Methods for Solving 7 x 2 x 3
There are several ways to approach this calculation, each highlighting different aspects of multiplication:
-
Sequential Multiplication: This is the most straightforward approach. We perform the operations sequentially, from left to right:
- 7 x 2 = 14
- 14 x 3 = 42
Therefore, 7 x 2 x 3 = 42
-
Commutative Property: The commutative property of multiplication states that the order of the factors does not affect the product. This means 7 x 2 x 3 is the same as 3 x 7 x 2, or any other permutation of the factors. We can exploit this to simplify the calculation:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 7 x 6 = 42
This method leverages smaller, easier multiplications to arrive at the same answer.
-
Associative Property: The associative property of multiplication allows us to group the factors differently without changing the product. This means (7 x 2) x 3 = 7 x (2 x 3). This property is particularly useful when dealing with more complex expressions.
-
Visual Representation: We can visualize this problem using arrays or groups. Imagine 7 rows of 2 objects each, and then imagine repeating that entire arrangement 3 times. Counting the total number of objects gives us the product, 42.
Factors, Multiples, and Prime Numbers: A Deeper Look
Let's analyze the factors involved: 7, 2, and 3.
-
7: This is a prime number, meaning it is only divisible by 1 and itself.
-
2: This is also a prime number. It's the only even prime number.
-
3: Another prime number.
Understanding the prime factorization of a number is crucial in various mathematical applications, including finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of numbers. In this case, the prime factorization of 42 (the product) is 2 x 3 x 7.
The multiples of each factor are:
-
Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49…
-
Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16…
-
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42…
Notice that 42 is a multiple of all three factors.
Real-World Applications: Beyond the Classroom
While seemingly basic, the concept behind 7 x 2 x 3, and multiplication in general, has far-reaching implications in numerous fields:
-
Engineering and Architecture: Calculating dimensions, material quantities, and structural load-bearing capacities. For example, calculating the volume of a rectangular prism requires multiplication of its length, width, and height.
-
Finance and Business: Calculating profits, losses, interest rates, and financial projections. Understanding multiplication is essential for managing budgets and making informed financial decisions.
-
Science and Technology: From physics and chemistry to computer science, multiplication is essential for analyzing data, performing calculations, and building models. In computer science, bit manipulation often involves multiplication for various operations.
-
Everyday Life: Calculating the total cost of multiple items, determining the number of items needed, or even dividing a recipe – multiplication is an integral part of our daily lives. For example, if you need 7 bags of apples, each containing 2 pounds of apples, and you want to buy 3 times that amount for the week, you would use multiplication to calculate the total amount needed.
Beyond the Calculation: Developing Mathematical Thinking
The simple equation 7 x 2 x 3 provides a springboard for developing crucial mathematical thinking skills:
-
Problem-solving: Understanding different methods to solve the same problem fosters flexibility and adaptability in tackling more complex mathematical challenges.
-
Critical thinking: Analyzing the properties of multiplication (commutative and associative) promotes critical thinking and a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts.
-
Pattern recognition: Observing patterns in multiples and factors helps develop pattern recognition skills, a valuable tool in mathematics and other fields.
-
Abstract reasoning: Understanding abstract mathematical concepts is crucial for advanced studies. The simple equation forms a foundational step in developing this skill.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the answer to 7 x 2 x 3? The answer is 42.
-
Why is the order of multiplication not important in this case? This is because of the commutative and associative properties of multiplication. The order of factors and their grouping does not affect the final product.
-
What if I have more than three factors? The same principles apply. Continue multiplying sequentially, or use the commutative and associative properties to simplify the calculation.
-
How can I improve my multiplication skills? Practice regularly with various problems, use different methods, and visualize the problems using diagrams or arrays.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of 7 x 2 x 3
The seemingly simple equation 7 x 2 x 3 offers a gateway to understanding the profound power and versatility of multiplication. It's not just about arriving at the answer 42; it's about grasping the underlying principles, exploring different approaches, and recognizing the far-reaching applications of this fundamental arithmetic operation. Mastering this foundational concept will build a strong base for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and foster crucial problem-solving and critical-thinking skills applicable across diverse fields. From engineering marvels to everyday budgeting, the significance of this seemingly simple equation extends far beyond the classroom, highlighting the enduring relevance of mathematical understanding in all aspects of life. By understanding the nuances and applications of even a simple equation like this one, we develop a deeper appreciation for the power and elegance of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 X 2 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.