Hcf Of 308 And 330
plugunplug
Sep 05, 2025 · 5 min read
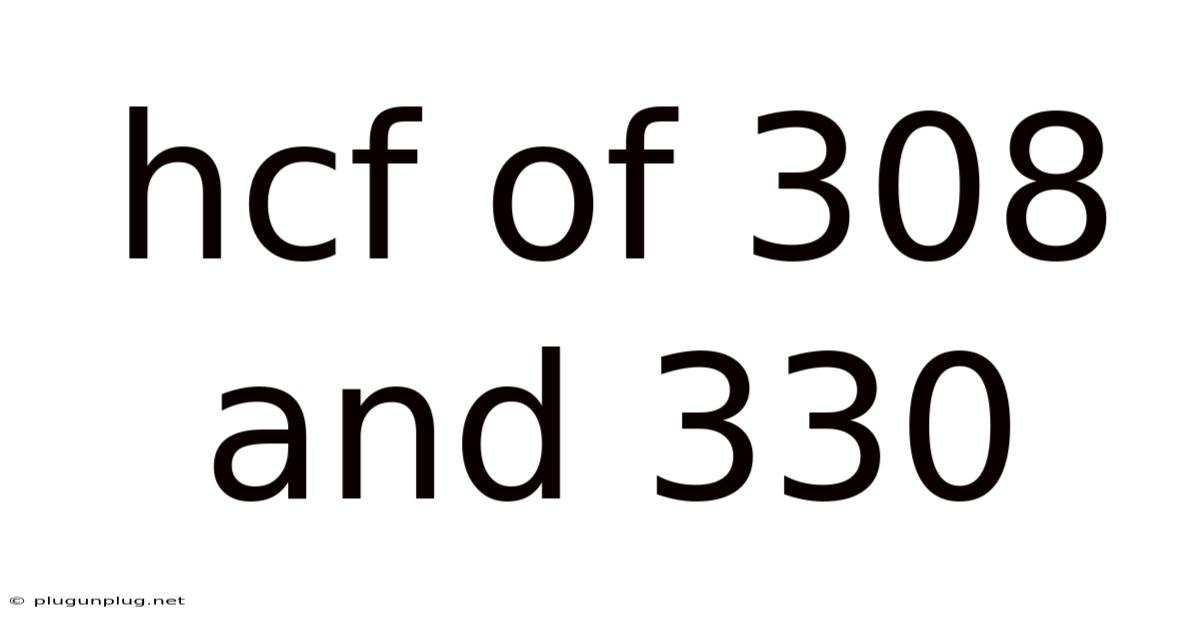
Table of Contents
Finding the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of 308 and 330: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the Highest Common Factor (HCF), also known as the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in number theory. This article will delve deep into the process of determining the HCF of 308 and 330, exploring various methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We'll cover everything from the prime factorization method to the Euclidean algorithm, ensuring you grasp the concept fully. Understanding HCF is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving algebraic problems, and understanding more advanced mathematical concepts.
Introduction: Understanding the Highest Common Factor (HCF)
The HCF of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of them without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that's a factor of both numbers. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The common factors of 12 and 18 are 1, 2, 3, and 6. Therefore, the highest common factor (HCF) of 12 and 18 is 6. This seemingly simple concept has far-reaching implications in mathematics and beyond.
Method 1: Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves. Then, we identify the common prime factors and multiply them to find the HCF. Let's apply this to 308 and 330:
Step 1: Prime Factorization of 308
We can break down 308 as follows:
308 = 2 x 154 = 2 x 2 x 77 = 2 x 2 x 7 x 11 = 2² x 7 x 11
Therefore, the prime factorization of 308 is 2² x 7 x 11.
Step 2: Prime Factorization of 330
Now let's find the prime factors of 330:
330 = 2 x 165 = 2 x 3 x 55 = 2 x 3 x 5 x 11
Therefore, the prime factorization of 330 is 2 x 3 x 5 x 11.
Step 3: Identifying Common Prime Factors
Comparing the prime factorizations of 308 and 330, we see that they share the prime factor 11. Both numbers contain at least one factor of 11. The prime factor 2 is present in 308 but not 330, same as the prime factors 3, 5, and 7 which are not present in both numbers.
Step 4: Calculating the HCF
The HCF is the product of the common prime factors. In this case, the only common prime factor is 11. Therefore:
HCF (308, 330) = 11
Method 2: The Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the HCF of two numbers. It's based on the principle that the HCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until we reach a point where the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the HCF.
Step 1: Repeated Subtraction (or Division)
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 308 and 330.
- Start with the larger number: 330
- Subtract the smaller number repeatedly: 330 - 308 = 22
- Now, the new pair of numbers is 308 and 22.
- Repeat the process: 308 ÷ 22 = 14 with a remainder of 0.
Step 2: Identifying the HCF
Since the remainder is 0, the last non-zero remainder (which was 22 in our previous step, but 0 in this step) in the division process is the HCF. However, we can see that 22 is not a factor of both 308 and 330. The correct use of the Euclidean algorithm with division should be:
330 = 1 x 308 + 22 308 = 14 x 22 + 0
Since the remainder is 0, the HCF is the divisor in the last step, which is 22. There seems to be a mistake in the previous explanation, let's review the calculation:
330 divided by 308 is 1 with remainder 22. 308 divided by 22 is 14 with remainder 0.
The last non-zero remainder is 22. Therefore:
HCF(308, 330) = 22
There was a calculation error in the previous example using the subtraction method. The division method within the Euclidean algorithm is more reliable.
Understanding the Importance of the HCF
The HCF finds applications in various areas, including:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The HCF allows us to reduce fractions to their simplest form. For example, the fraction 308/330 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their HCF (22), resulting in the simplified fraction 14/15.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: Understanding HCF can be vital in solving certain types of algebraic equations, particularly those involving factorization.
-
Geometric Problems: HCF can be used in problems related to finding the largest possible square tiles that can be used to cover a rectangular floor completely. For example, if a floor measures 308 cm by 330 cm, the largest square tile would have sides measuring the HCF of 308 and 330 (22 cm).
-
Number Theory: HCF plays a fundamental role in various number theory concepts, such as modular arithmetic and cryptography.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What if the HCF of two numbers is 1?
A: If the HCF of two numbers is 1, it means the numbers are relatively prime or coprime. They have no common factors other than 1.
Q: Can the HCF of two numbers be greater than either of the numbers?
A: No, the HCF can never be greater than the smaller of the two numbers.
Q: Which method is better, prime factorization or the Euclidean algorithm?
A: The Euclidean algorithm is generally more efficient, especially for larger numbers, as it avoids the sometimes lengthy process of prime factorization.
Conclusion: Mastering HCF Calculations
Finding the HCF of two numbers, like 308 and 330, is a fundamental skill in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. Both the prime factorization method and the Euclidean algorithm are valuable tools for determining the HCF. While prime factorization provides a deeper understanding of the number's structure, the Euclidean algorithm offers a more efficient approach, particularly for larger numbers. Mastering these methods will strengthen your mathematical foundation and open doors to understanding more complex mathematical concepts. Remember that understanding the underlying principles is as crucial as mastering the techniques themselves. Through consistent practice and a thorough understanding of these methods, you can confidently tackle HCF problems and appreciate the elegance and utility of this fundamental concept.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Hcf Of 308 And 330 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.