Hcf Of 42 And 90
plugunplug
Sep 05, 2025 · 6 min read
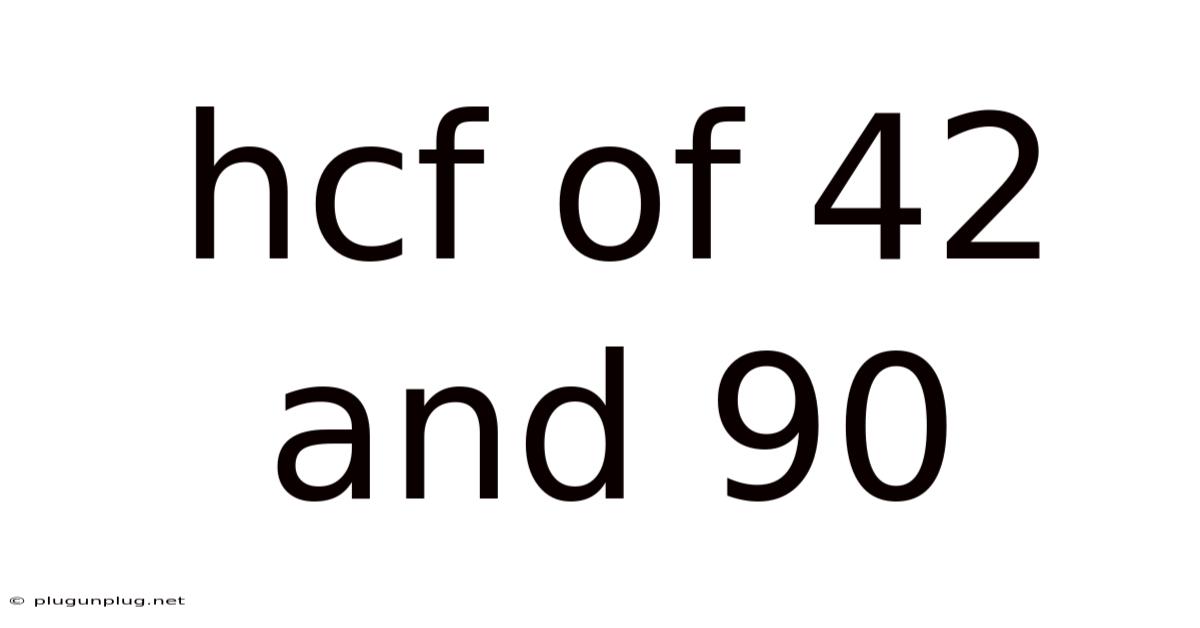
Table of Contents
Finding the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of 42 and 90: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the highest common factor (HCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics. This guide will explore various methods to determine the HCF of 42 and 90, providing a detailed explanation suitable for learners of all levels. We'll delve into the underlying principles, explore different approaches, and answer frequently asked questions to solidify your understanding of this important mathematical concept.
Introduction to Highest Common Factor (HCF)
The highest common factor (HCF) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of them without leaving a remainder. Understanding HCF is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving problems involving ratios, and performing other mathematical operations. In this article, we'll focus on finding the HCF of 42 and 90, illustrating multiple methods to achieve this. We’ll also discuss the prime factorization method, the division method, and the Euclidean algorithm, comparing their effectiveness and highlighting their applications.
Method 1: Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – the smallest prime numbers that multiply together to give the original number. Let's start by finding the prime factors of 42 and 90:
Prime Factorization of 42:
42 = 2 × 21 = 2 × 3 × 7
Prime Factorization of 90:
90 = 2 × 45 = 2 × 3 × 15 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 = 2 × 3² × 5
Once we have the prime factorization of both numbers, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers. In this case:
- Both 42 and 90 have a common factor of 2.
- Both 42 and 90 have a common factor of 3.
The lowest power of 2 is 2¹ (or simply 2), and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, the HCF of 42 and 90 is the product of these common prime factors raised to their lowest powers:
HCF(42, 90) = 2 × 3 = 6
Therefore, the highest common factor of 42 and 90 is 6. This means that 6 is the largest number that divides both 42 and 90 without leaving a remainder.
Method 2: Division Method
The division method is an iterative process that involves repeatedly dividing the larger number by the smaller number until the remainder is zero. The last non-zero remainder is the HCF.
-
Divide the larger number (90) by the smaller number (42):
90 ÷ 42 = 2 with a remainder of 6
-
Replace the larger number with the smaller number (42) and the smaller number with the remainder (6):
42 ÷ 6 = 7 with a remainder of 0
Since the remainder is now 0, the last non-zero remainder (6) is the HCF. Therefore, the HCF(42, 90) = 6.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the HCF of two numbers. It's based on the principle that the HCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, and that number is the HCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to find the HCF of 42 and 90:
-
Start with the two numbers: 42 and 90
-
Subtract the smaller number from the larger number: 90 - 42 = 48. Now we have 42 and 48.
-
Repeat the subtraction: 48 - 42 = 6. Now we have 42 and 6.
-
Repeat again: 42 - 6 = 36. Now we have 6 and 36.
-
Repeat: 36 - 6 = 30. Now we have 6 and 30.
-
Repeat: 30 - 6 = 24. Now we have 6 and 24.
-
Repeat: 24 - 6 = 18. Now we have 6 and 18.
-
Repeat: 18 - 6 = 12. Now we have 6 and 12.
-
Repeat: 12 - 6 = 6. Now we have 6 and 6.
Since both numbers are now equal to 6, the HCF(42, 90) = 6.
While the repeated subtraction is conceptually clear, the Euclidean algorithm is often presented more efficiently using a series of divisions with remainders:
- Divide 90 by 42: 90 = 2 × 42 + 6
- Divide 42 by the remainder 6: 42 = 7 × 6 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 6, so the HCF(42, 90) = 6. This method is significantly faster than repeated subtraction, especially for larger numbers.
Comparing the Methods
All three methods – prime factorization, division, and the Euclidean algorithm – lead to the same result: the HCF of 42 and 90 is 6. However, each method has its strengths and weaknesses:
-
Prime Factorization: This method is conceptually simple and easy to understand, particularly for smaller numbers. However, it can become cumbersome for large numbers where finding prime factors can be challenging.
-
Division Method: This method is relatively straightforward and efficient for numbers of moderate size. It's easier to perform than repeated subtractions within the Euclidean algorithm.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This method is the most efficient, especially for large numbers. It converges to the HCF quickly and avoids the need to find prime factors.
Applications of HCF
The concept of HCF has numerous applications in various fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the HCF of the numerator and denominator allows you to simplify a fraction to its lowest terms. For example, the fraction 42/90 can be simplified to 7/15 by dividing both numerator and denominator by their HCF (6).
-
Solving Ratio Problems: HCF is used to simplify ratios to their simplest form. For example, a ratio of 42:90 can be simplified to 7:15.
-
Dividing Quantities Equally: HCF helps determine the largest possible equal parts into which two quantities can be divided. For example, you can divide 42 apples and 90 oranges into 6 equal groups, each with 7 apples and 15 oranges.
-
Geometric Problems: HCF is used in geometry problems involving finding the greatest common measure of lengths or areas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the HCF of two numbers is 1?
A1: If the HCF of two numbers is 1, the numbers are said to be relatively prime or coprime. This means they share no common factors other than 1.
Q2: Can I use a calculator to find the HCF?
A2: Yes, many calculators have built-in functions to find the HCF (or GCD) of two or more numbers. However, understanding the underlying methods is crucial for a deeper mathematical understanding.
Q3: How do I find the HCF of more than two numbers?
A3: You can extend any of the methods described above to find the HCF of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you find the prime factors of all the numbers and identify the common factors with their lowest powers. For the Euclidean algorithm, you find the HCF of two numbers, then find the HCF of the result and the next number, and so on.
Conclusion
Finding the highest common factor of two numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics with broad applications. We have explored three effective methods: prime factorization, the division method, and the Euclidean algorithm, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. While calculators can assist with calculations, understanding the underlying principles is essential for solving more complex problems and developing a strong mathematical foundation. The ability to efficiently compute the HCF is a valuable tool in various mathematical contexts, from simplifying fractions to solving more advanced problems in number theory and other related fields. By mastering these methods, you'll gain a deeper understanding of number theory and improve your problem-solving abilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Hcf Of 42 And 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.