Height X Width X Depth
plugunplug
Sep 24, 2025 · 7 min read
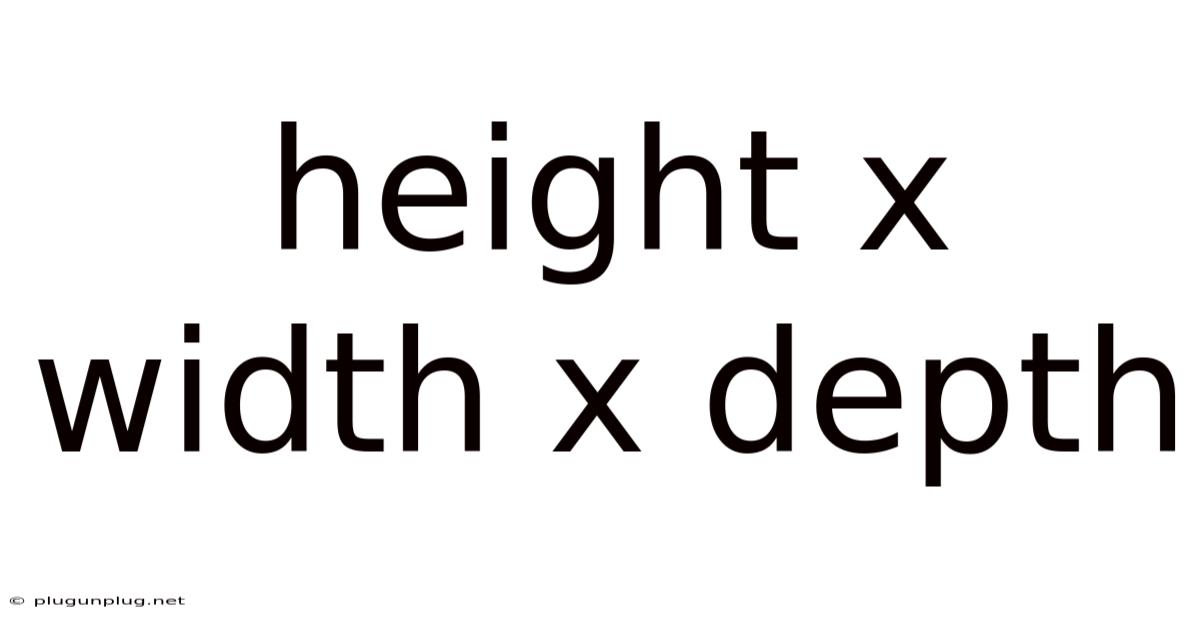
Table of Contents
Understanding Height x Width x Depth: A Comprehensive Guide to Three-Dimensional Measurement
Understanding the dimensions of height, width, and depth is fundamental to numerous fields, from everyday life to advanced scientific applications. This comprehensive guide will explore these three crucial measurements, explaining their definitions, applications, and the importance of understanding their interrelationship. We will delve into practical examples and address frequently asked questions, ensuring a complete understanding for readers of all backgrounds.
Introduction: Defining the Three Dimensions
Height, width, and depth represent the three spatial dimensions necessary to define the size and volume of any three-dimensional object. While often used interchangeably in casual conversation, understanding their precise definitions is crucial for accurate measurements and calculations.
-
Height: Typically refers to the vertical dimension of an object, the distance from its base to its highest point. Think of it as how tall something is. However, the orientation of "height" can be relative to the context. What is considered height in one situation (like the height of a building) might be considered depth in another (like the depth of a box lying on its side).
-
Width: Represents the horizontal dimension of an object, measured across its widest point. Think of it as how broad or wide something is. Again, the perspective of "width" is context-dependent.
-
Depth: Is also a horizontal dimension, but it typically refers to the distance from front to back, or the thickness of an object. It is often used in contexts where an object extends inwards.
These definitions are relative and dependent on the object's orientation and the context in which they are used. A box, for instance, might have a height, width, and depth, but if we rotate the box, these values will change their labels relative to their new orientation. This highlights the importance of clear communication and consistent referencing when dealing with these measurements.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
The application of height, width, and depth measurements spans numerous fields:
-
Construction and Engineering: Accurate measurements are crucial for designing and building structures, from houses and bridges to skyscrapers and dams. Incorrect measurements can lead to structural instability and safety hazards. Engineers utilize these dimensions for load calculations, material estimations, and ensuring compliance with building codes.
-
Manufacturing and Production: Height, width, and depth are essential in manufacturing processes for creating parts and products with precise dimensions. In industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics, even slight discrepancies can affect functionality and performance. These measurements are crucial for creating molds, tools, and assembly lines.
-
Packaging and Shipping: Determining the dimensions of products is critical for efficient packaging and shipping. Knowing the height, width, and depth helps determine the appropriate box size, optimize space utilization during transport, and calculate shipping costs accurately. This is particularly relevant in e-commerce, where accurate dimensions are crucial for smooth delivery.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: In medical imaging (like MRI and CT scans), accurate measurements of organs and tissues are critical for diagnosis and treatment planning. Height, weight, and other body dimensions are also crucial for assessing a patient's overall health and guiding medical interventions.
-
Computer Graphics and 3D Modeling: In the digital world, height, width, and depth are fundamental concepts for creating three-dimensional models and animations. 3D artists utilize these dimensions to define the size and shape of objects, influencing their appearance and interaction within virtual environments. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for creating realistic and believable 3D models.
-
Geography and Cartography: Elevation (height above sea level) is a crucial aspect of geographical data, used to create maps, models, and understand terrain. The depth of bodies of water is also essential for navigation and understanding oceanographic processes. Using height, width, and depth in various combinations allows us to represent the world's surface in three dimensions, effectively showing the landforms and the various features on the earth's surface.
Practical Examples: Illustrating the Concepts
Let's examine a few practical examples to solidify our understanding:
-
Calculating the volume of a rectangular prism: The volume of a rectangular prism (a box-shaped object) is calculated by multiplying its height, width, and depth: Volume = Height x Width x Depth. If a box has a height of 10 cm, a width of 5 cm, and a depth of 3 cm, its volume is 150 cubic centimeters (10 cm x 5 cm x 3 cm = 150 cm³).
-
Estimating the amount of paint needed for a wall: To calculate the amount of paint needed to cover a wall, you would first need to determine its height and width. Then you would multiply those measurements to find the area of the wall. This would then be used along with the coverage rate of the paint to estimate the quantity needed for a single coat or multiple coats if required.
-
Determining the size of a shipping container: Shipping companies use height, width, and depth measurements to determine the size of containers and optimize space utilization on ships and trucks. Accurate measurements ensure that goods are packed efficiently and transported safely.
-
Designing a furniture piece: An interior designer or furniture maker would use height, width, and depth measurements to create a design that fits the available space and meets the functional requirements. They would also consider ergonomics and aesthetics, ensuring comfort and visual appeal.
Beyond Simple Measurements: Advanced Applications
The concepts of height, width, and depth extend beyond simple linear measurements. They are used in more complex calculations and analyses:
-
Volume and Capacity: As demonstrated with the rectangular prism, height, width, and depth are crucial in calculating the volume or capacity of various shapes, including irregular objects through techniques like water displacement or 3D scanning.
-
Surface Area Calculations: Understanding these dimensions is also necessary for calculating the surface area of objects, vital in applications like painting, wrapping, and heat transfer calculations.
-
Coordinate Systems: In three-dimensional coordinate systems (like Cartesian coordinates), height, width, and depth are represented by the x, y, and z axes, respectively. These systems are fundamental in computer graphics, physics, and engineering simulations.
-
Spatial Reasoning and Problem Solving: A strong understanding of these three dimensions is essential for developing spatial reasoning skills, which are critical in various fields including architecture, engineering, and even everyday tasks like packing a suitcase.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if an object is irregular in shape? How do I measure its height, width, and depth?
A1: Measuring irregular objects requires more sophisticated techniques. For simpler objects, you might use flexible measuring tapes or rulers to approximate the dimensions at their widest points. For more accurate measurements, you might use 3D scanning technologies, which can create a digital model and provide precise dimensions.
Q2: Are there standard units of measurement for height, width, and depth?
A2: Yes, the most common units are metric (millimeters, centimeters, meters) and imperial (inches, feet, yards). The choice of units depends on the application and the context. It's crucial to maintain consistency in the unit of measurement used for all dimensions to prevent errors in calculations.
Q3: How important is precision in measuring height, width, and depth?
A3: The level of precision required depends on the application. For some applications, rough estimations might suffice, while others (like precision engineering) require extremely accurate measurements down to fractions of a millimeter. Always aim for the necessary precision required by the specific task to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Q4: Can height, width, and depth be negative values?
A4: In standard measurement systems, height, width, and depth are generally considered positive values. Negative values might be used in specific contexts like coordinate systems to denote position relative to a reference point, but in general calculations of size and volume, they are not applicable.
Conclusion: Mastering Three-Dimensional Measurement
Mastering the concepts of height, width, and depth is crucial for a wide range of disciplines and everyday tasks. Understanding their definitions, applications, and interrelationships allows for accurate measurements, efficient problem-solving, and innovation across diverse fields. From calculating the volume of a box to designing complex engineering structures, a thorough grasp of these three fundamental dimensions is indispensable for success in many endeavors. The importance of accurate measurements, appropriate units, and clear communication cannot be overstated when working with these critical parameters. By understanding these core concepts, you will be equipped to tackle a wide range of challenges that require precise three-dimensional analysis.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Height X Width X Depth . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.